HBase, as a powerful distributed database system built on top of Hadoop, plays a crucial role in managing large-scale structured data. At the core of HBase’s architecture lies the hmaster, a vital component responsible for coordinating region assignments, fault tolerance, and cluster management. In complex environments where data needs to be handled across multiple nodes, HMaster ensures that the system remains scalable and reliable. This article explores the key responsibilities of HMaster and other essential components within the HBase architecture, such as RegionServer, ZooKeeper, and HDFS, and their collaborative roles in ensuring optimal system performance.
HMaster’s Definition and Core Responsibilities
HMaster plays a crucial role in HBase architecture, managing the distributed HBase system built on top of Hadoop’s HDFS to handle large-scale structured data. As the primary node, HMaster oversees region assignment, ensuring that data is evenly distributed across RegionServers for efficient storage and access. Its responsibilities extend to load balancing, fault recovery, and metadata management. Additionally, HMaster handles cluster expansion and contraction, automatically assigning regions to new nodes when needed, and recovering data from failed RegionServers, providing resilience against hardware failures. This makes HMaster the command center of the HBase cluster, ensuring the system’s scalability and reliability. For instance, in a large e-commerce company processing millions of transactions daily, HMaster optimizes performance by balancing the data load across RegionServers, ensuring smooth system operations.
Core Components of HBase Architecture
Apart from HMaster, other key components in HBase architecture include RegionServer, ZooKeeper, and HDFS. Each of these components plays a distinct role in ensuring the efficient operation of the system.
The Role and Function of RegionServer
RegionServer is the component responsible for storing and managing data in HBase. It handles client requests for reading and writing data and stores the data in different regions of HBase tables. Each RegionServer manages multiple regions, which are assigned by HMaster during the startup process. RegionServer’s primary functions include handling data reads and writes, managing memory caches, and maintaining logs. When new data is written, it is first stored in a memory cache called MemStore and logged in a Write-Ahead Log (WAL) to prevent data loss in case of a system crash. Once the memory cache is full, the data is flushed to disk in HFile format. The performance of RegionServer is crucial for the overall performance of HBase since it directly affects data read and write speeds, as well as the reliability of the system. For instance, consider a financial institution processing real-time transactions. The RegionServer is responsible for handling massive amounts of transactional data efficiently while ensuring that every transaction is properly logged and backed up.
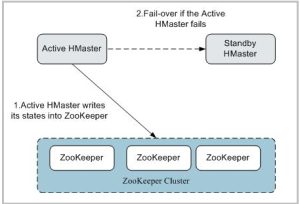
The Importance of ZooKeeper in HBase
ZooKeeper acts as the coordinator in HBase, responsible for maintaining the distributed state of the system and ensuring synchronization across multiple nodes. As a distributed system, HBase requires coordination between various nodes, and ZooKeeper plays a critical role by maintaining metadata and coordinating actions across the cluster. For example, ZooKeeper keeps track of the states of HMaster and RegionServers, assisting HMaster in assigning regions. When a RegionServer crashes, ZooKeeper notifies HMaster, triggering the fault recovery mechanism. In this sense, ZooKeeper serves as the “traffic controller” of HBase, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance across the system. Furthermore, ZooKeeper plays a critical role in electing the active HMaster, ensuring that the cluster always has an operational master node to manage and direct its resources.Without ZooKeeper, HBase would struggle to maintain the synchronization required for optimal performance in a distributed environment, making it a cornerstone of the HBase architecture.

How HDFS Supports HBase Storage
HBase is built on top of Hadoop’s HDFS, which provides the underlying storage for all HBase data. HDFS is a reliable and distributed file system that splits data into blocks and distributes these blocks across different nodes in the system, ensuring redundancy and fault tolerance. HDFS’s architecture is designed to handle large volumes of data, which makes it ideal for HBase’s needs. It ensures that HBase can store massive amounts of tabular data across multiple nodes in a cluster. By providing data replication, HDFS ensures that even if a node fails, the data remains accessible from other replicas. HDFS also makes it easy for HBase to perform efficient data backup and restoration, providing another layer of reliability for enterprise applications. For example, a social media platform that needs to store and access petabytes of user data in real time relies on HDFS to distribute and safeguard that data. In this case, HDFS would ensure that the data is both distributed across multiple nodes and replicated to prevent loss.
The Collaborative Mechanism Between HMaster and RegionServer
The collaboration between HMaster and RegionServer is essential for HBase’s smooth operation. HMaster allocates and reassigns regions, while RegionServer manages data storage. At the cluster’s start, HMaster assigns regions to RegionServers. During write operations, RegionServers process data independently, with HMaster overseeing region placement and status. If a RegionServer crashes, HMaster quickly reallocates its regions to maintain service and prevent data loss. For instance, in a data analytics company using HBase for customer interaction data, HMaster ensures uninterrupted service by reallocating regions if a server fails. Additionally, HMaster monitors RegionServer loads and triggers load balancing when needed, redistributing regions to improve performance and enhance fault tolerance.
Conclusion
HBase is a distributed database system that relies on core components—HMaster, RegionServer, ZooKeeper, and HDFS—each contributing to its efficiency, scalability, and reliability. HMaster manages tasks like region assignment, RegionServer handles data storage, ZooKeeper coordinates the system, and HDFS provides data storage. In applications like telecom companies managing large customer datasets, these components work together to ensure efficient data handling while maintaining fault tolerance and high availability. For example, Huawei’s iMaster NCE-CampusInsight helps detect network issues proactively, similar to how HBase uses ZooKeeper and HMaster for fault detection, ensuring system uptime and performance. Understanding how these core components work in HBase provides a solid foundation for managing and optimizing large-scale data systems.

